JPA Relationship
JPA Entity Relationship?
DB에서는 fk로 일대다, 다대일 관계가 연결이 되지만 JPA 에서의 Entity 관계는 크게 4가지 종류로 표현된다.
- @ManyToOne
- @OneToOne
- @OneToMany
- @ManyToMany
Entity는 JPA진영에서 Database의 테이블의 한 로우 해당하는 객체이다.
Entity로 인해 객체와 테이블이 Mapping되어 관리되는 ORM의 핵심이라고 볼 수 있다.
다음 예제를 통해 관계에 대해 자세히 알아보겠다.
Example
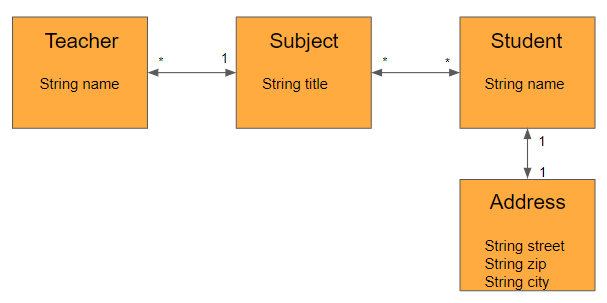
@ManyToOne 여러 선생님이 한 과목을 맡을 수 있다. 선생님과 과목은 다대일 관계 이다.
@OneToOne 학생과 주소는 일대일 관계이다.
@OneToMany 과목은 여러 선생님이 담당한다. 일대다 관계이다.
@ManyToMany 학생은 여러 과목을 가지고 과목에 여러 수강생이 있다. 다대다 관계이다.
ManyToOne and OneToMany
참고 문서 : https://www.objectdb.com/api/java/jpa/ManyToOne
참고 문서 : https://www.objectdb.com/api/java/jpa/OneToMany
@ManyToOne은 다대일 관계에서 다 쪽에서 참조를 이용할 때 사용한다.
@JoinColumn annotation과 함께 사용하여 조인될 테이블 정보를 알려준다.
@ManyToOne 속성
@OneToMany는 일대다 관계에서 일 쪽에서 List, Set으로 다 쪽을 관리할 때 사용한다.
기본적으로 다 쪽에서 Insert, Update에 대한 권리를 가지고 (연관관계의 주인)
One은 mappedBy를 통해 Read Only 속성을 가진다.
// Many 부분
@Entity
public class Teacher {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "teacher_id")
private Long id;
private String name;
@ManyToOne // 기본 FetchType은 EAGER이다.
private Subject subject;
}
// One 부분
@Entity
public class Subject {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "subject_id")
private Long id;
private String title;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "id") // 조회만 가능하게 한다.
private Set<Teacher> teacherList = new HashSet<>();
}
ManyToOne은 참조값 하나만 연결하면 되고 OneToMany는 참조를 List, Set으로 관리한다.
(Map도 가능하지만 설정이 복잡하다.) 일반적으로 구현체를 바로 생성해준다.
Main에서 사용하는 법을 확인해보자.
public static void logic(EntityManager em) throws Exception {
Subject math = new Subject("math");
em.persist(math);
Teacher teacherA = new Teacher("teacherA");
teacherA.setSubject(math);
em.persist(teacherA);
Teacher teacherB = new Teacher("teacherB");
teacherB.setSubject(math);
em.persist(teacherB);
// 조회 영역
System.out.println("■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■");
System.out.println("teacherA = " + teacherA);
System.out.println("teacherB = " + teacherB);
System.out.println("math = " + math);
System.out.println("■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■");
}
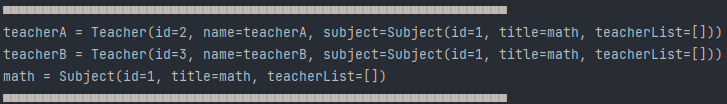
teacherA와 B 모두 Math를 담당하게 join이 되었다. 다만 이 코드는 문제가 발생한다.
👏Console
👏Database
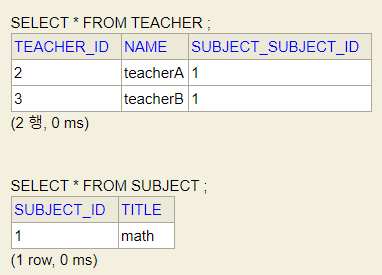
console창에는 1차캐쉬에 있는 것을 조회하기 때문에 Subject의 teacherList에 포함되어 있어야 하는 teacherA와 teacherB가 없다.
따라서 setSubject method를 수정하거나 따로 추가하는 method를 만들어야 한다.
// 수정 setSubject 대신 addSubject를 만들었다.
public void addSubject(Subject subject) {
setSubject(subject);
Set<Teacher> teacherList = subject.getTeacherList();
if(!teacherList.contains( subject )){
teacherList.add(this);
}
}
DB와 Console(1차 캐시)이 일치된 모습이다.
👏Console2
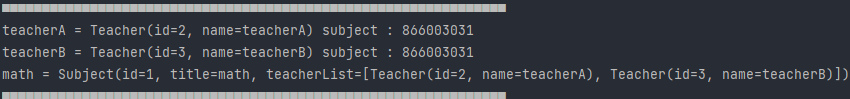
‼하지만 아직도 오류는 발생한다.
teacherA 가 math에서 english로 변경한다고 생각해보자.
Subject math = new Subject("math");
em.persist(math);
Teacher teacherA = new Teacher("teacherA");
teacherA.addSubject(math);
em.persist(teacherA);
👏addSubject(math)
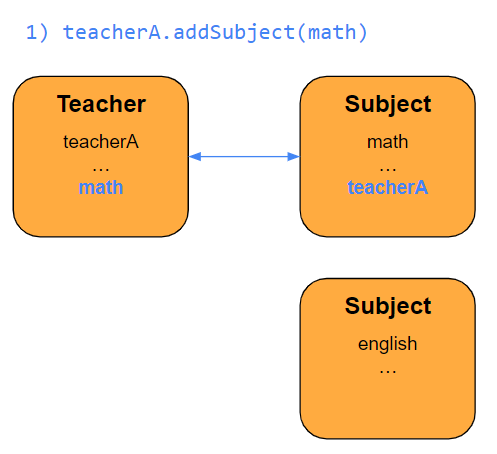
여기까진 잘 동작한다. teacherA의 subject를 math에서 english로 바꿔보자.
...
Subject english = new Subject("english");
em.persist(english);
teacherA.addSubject(english);
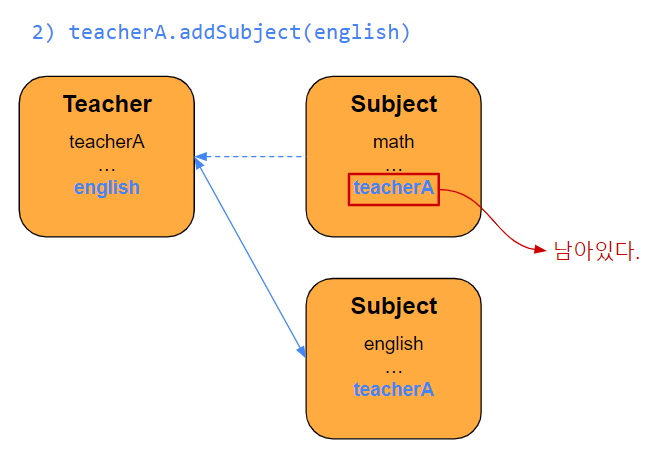
기존의 teacherA의 subject는 english로 잘 바뀌었지만 양방향 관계에서 math에 여전히 teacherA가 남아있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
setSubject을 하기 전 기존 teacher에 subject가 있다면 지워줘야한다.
// 최종 메서드
public void addSubject(Subject subject) {
if(this.subject != null) { // 기존에 연관관계가 있으면 삭제해야 한다.
this.subject.getTeacherList().remove(this);
}
setSubject(subject);
Set<Teacher> teacherList = subject.getTeacherList();
if(!teacherList.contains( subject )){
teacherList.add(this);
}
}
이제 잘 동작하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
ManyToMany
@ManyToMany
공식문서 https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/persistence/ManyToMany.html
@ManyToMany annotation을 붙여 다대다 연결관계를 만들 수 있음.
(하지만 실무에서 사용하지는 않는다. 실무는 다대일 관계 2개로 연결)
👏하지만 JPA 기본 스펙이니 예제로 보자.
// Subject
@Entity
public class Subject {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "subject_id")
private Long id;
private String title;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "subjects") // 연관관계의 주인을 하나로 정한다.
private List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
}
// Student
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "student_id")
private Long id;
private String name;
@ManyToMany
private Set<Subject> subjects = new HashSet<>();
public void addSubject(Subject subject) {
subjects.add(subject);
}
}
// Main
public static void logic(EntityManager em) throws Exception {
Subject math = new Subject("math");
em.persist(math);
Subject english = new Subject("english");
em.persist(english);
Student studentA = new Student("studentA");
em.persist(studentA);
Student studentB = new Student("studentB");
em.persist(studentB);
studentA.addSubject(math);
studentA.addSubject(english);
studentB.addSubject(english);
System.out.println("■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■");
System.out.println("studentA = " + studentA);
System.out.println("studentB = " + studentB);
System.out.println("math = " + math);
System.out.println("english = " + english);
System.out.println("■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■");
}
결과
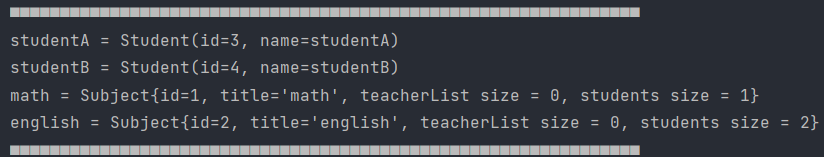
👏Console
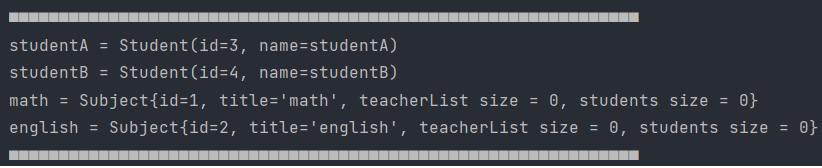
👏Database
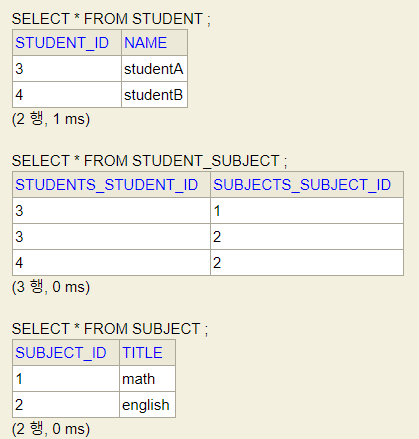
역시 결과는 1차 캐시와 DB가 동기화가 되지 않았다. addSubject에 처리를 더 해주자.
public void addSubject(Subject subject) {
subject.getStudents().add(this);
subjects.add(subject);
}
결과
👏Console
OneToOne
공식문서 https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/persistence/OneToOne.html
일대일 관계는 연관관계의 주인을 어느쪽에 해도 상관 없지만 확장성을 고려하여 다 쪽으로 변경될 수 있는 쪽에 주인을 하는것이 좋다.
// Address
@Entity
public class Address {
...
@OneToOne(mappedBy = "address")
private Student student;
...
}
// Student
@Entity
public class Student {
...
@OneToOne
private Address address;
...
}
//main
...
Student studentA = new Student("studentA");
em.persist(studentA);
Student studentB = new Student("studentB");
em.persist(studentB);
Address address1 = new Address("munjeoug", "158-200", "seoul");
em.persist(address1);
Address address2 = new Address("garak", "129-120", "seoul");
em.persist(address2);
studentA.setAddress(address1);
studentB.setAddress(address2);
...
결과
👏Console
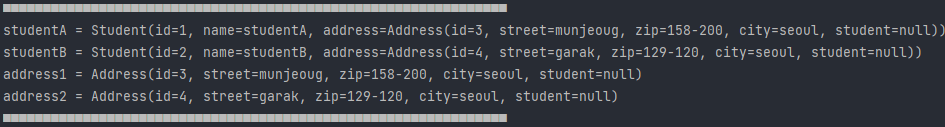
👏Database
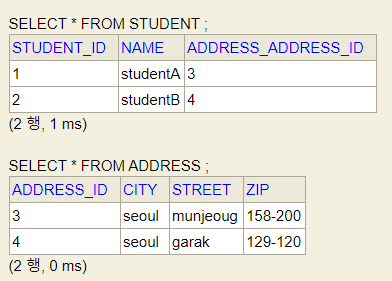
연관관계의 주인 쪽에서 외래 키 를 관리하는 것을 알 수 있다.
Reference
공식 문서 https://www.objectdb.com/api/java/jpa/annotations/relationship

댓글남기기